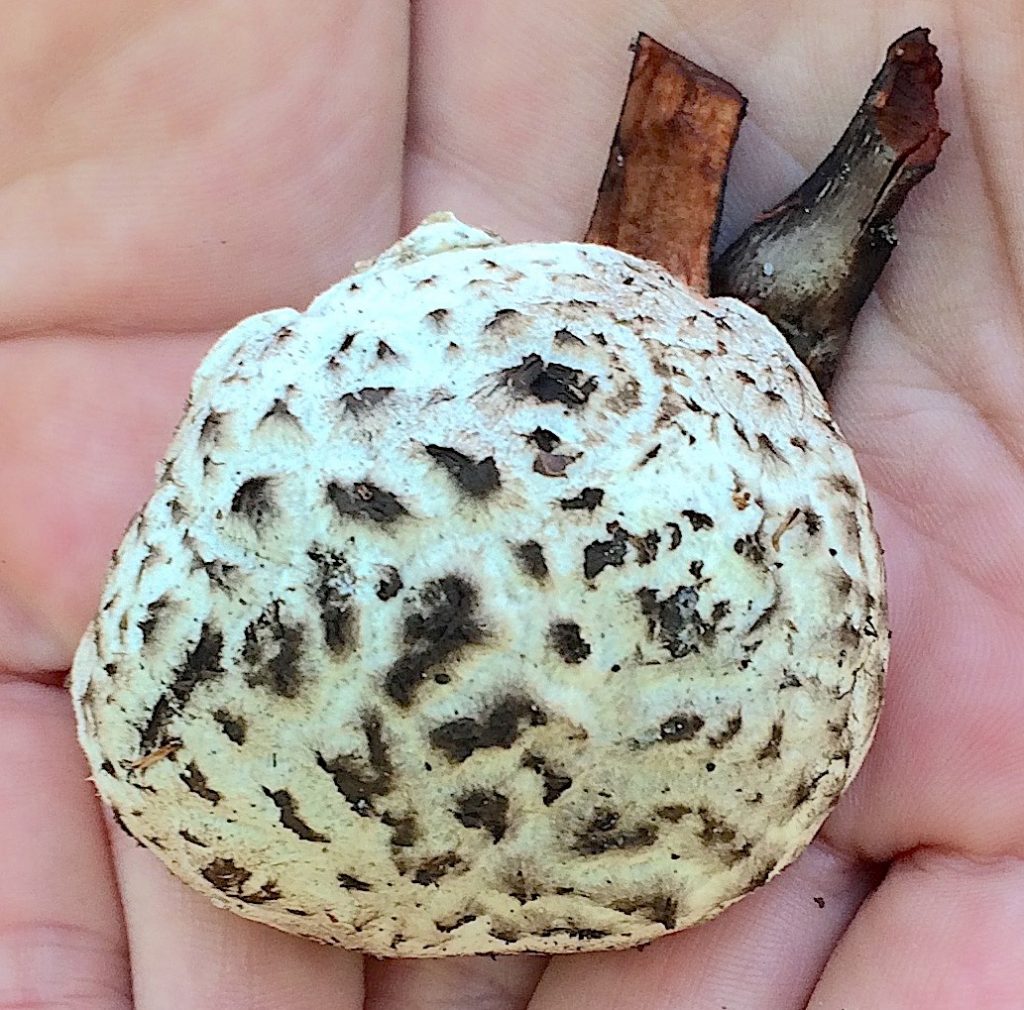

If you are in the habit of eating wild mushroom then you’re waiting for the spring rains. Local this usually happens in latter April or early May. That and warmer ground temperature tells mushrooms to grow. As a prelude I had my first edible wild mushroom find of the season this week.
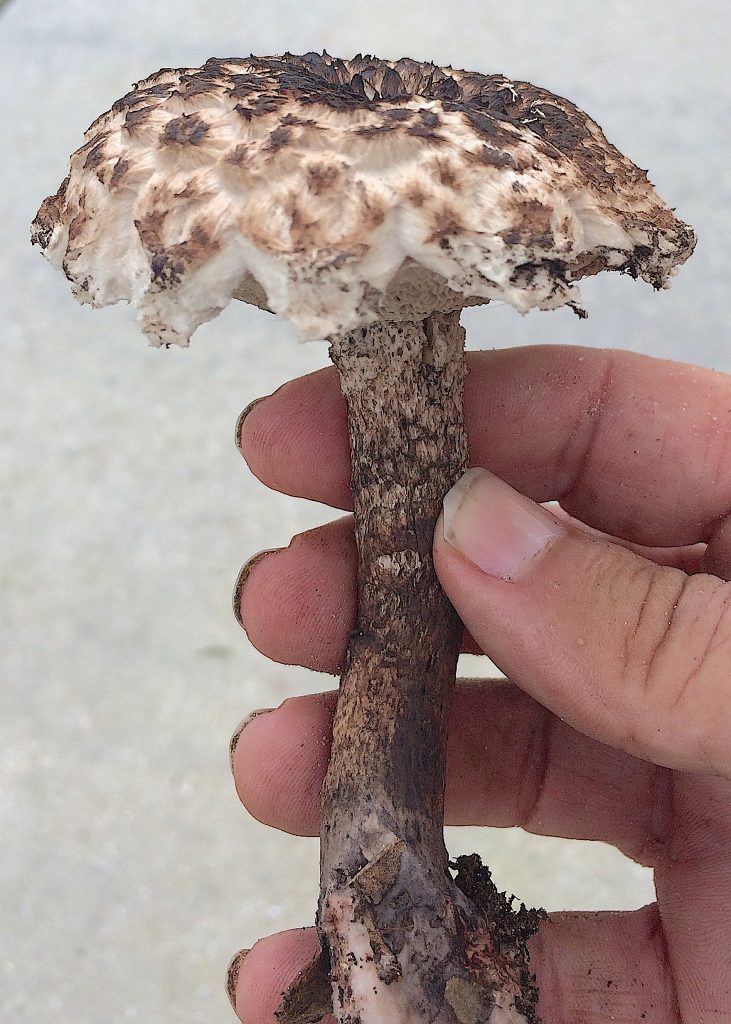

Old Man of the Woods, Strobilomyces sp. is a rather distinct mushroom. There are a few variations — a microscope helps to sort them out — but they are all edible. There are at least three species in North America and are in a group of mushrooms called Boletes. These mushrooms do not have gills but rather pores on the underside. The saving grace is none of them cause lasting organ damage if you eat a toxic one. There is a short check list one can use to tell if a Bolete is a potential edible. In Europe most of the Boletes are edible, in North America most are not, and in The South if not Florida many are unidentified. Opinions vary on the Old Men. Some cook and eat the entire mushroom. Others just the cap with pores throwing away the stems, others just the cap throwing away the pores, and some not liking the texture dry the pore-less cap, powder it, and use it for flavoring. I like the cap with pores fried which is how I cooked the one at the top of the newsletter. To me they taste like Porcini mushroom. The only drawback is you find only one or two at a time.
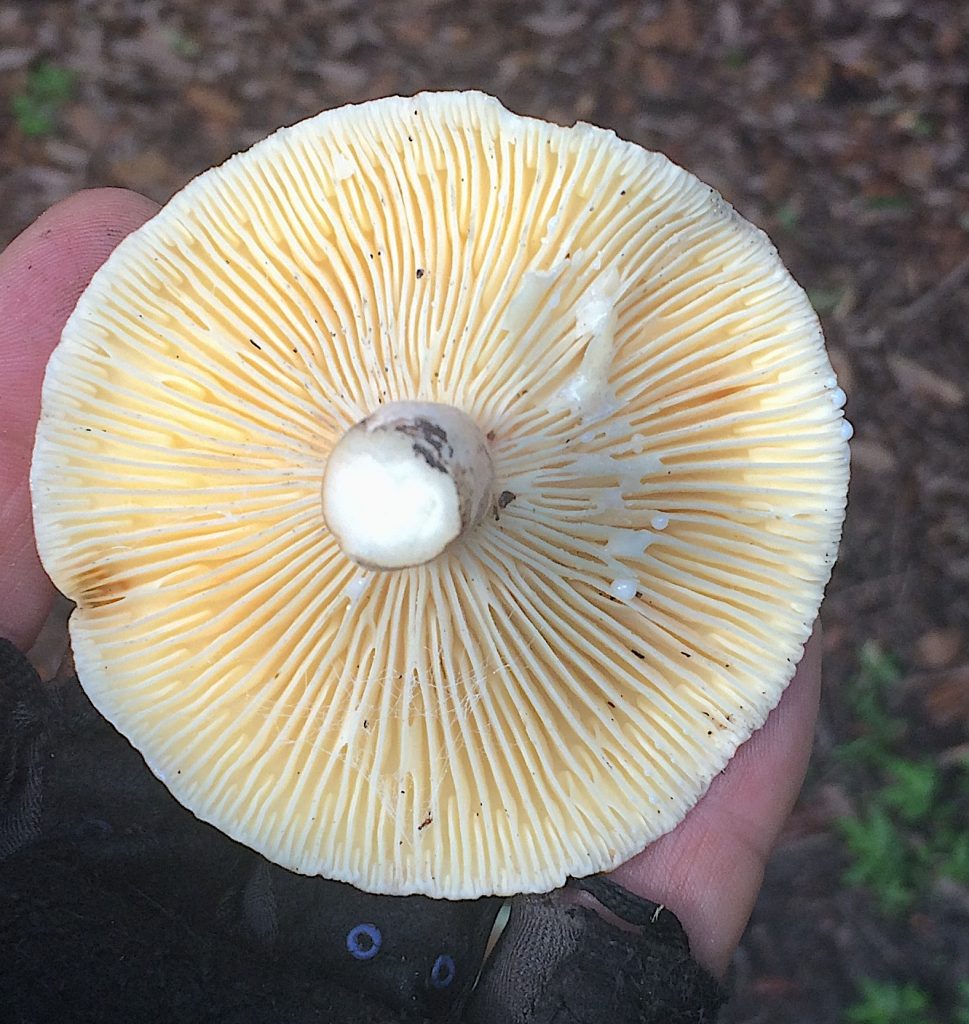

One local trio of edible mushroom we are waiting for are called “Milk Caps.” When broken or scraped all three weep a liquid, often white. It is not a latex but is called that. The liquid, however, can also be light yellow or watery. That the mushroom is the weeping helps you identify the genus, sometimes the species. Common locally is the Lactifluus hygrophorides, L. corrugis, L. volemus var. volemus and L. luteolus. The latter is edible but smells strongly like a dead fish. I picked some twelve pounds of them last year. They’re a substantial mushroom with a good flavor and texture. They are also fairly easy to identify. It has a ruddy cap, slightly felt-like to touch, wide-space gills, and bleeds a white fluid that does not stain the mushroom.
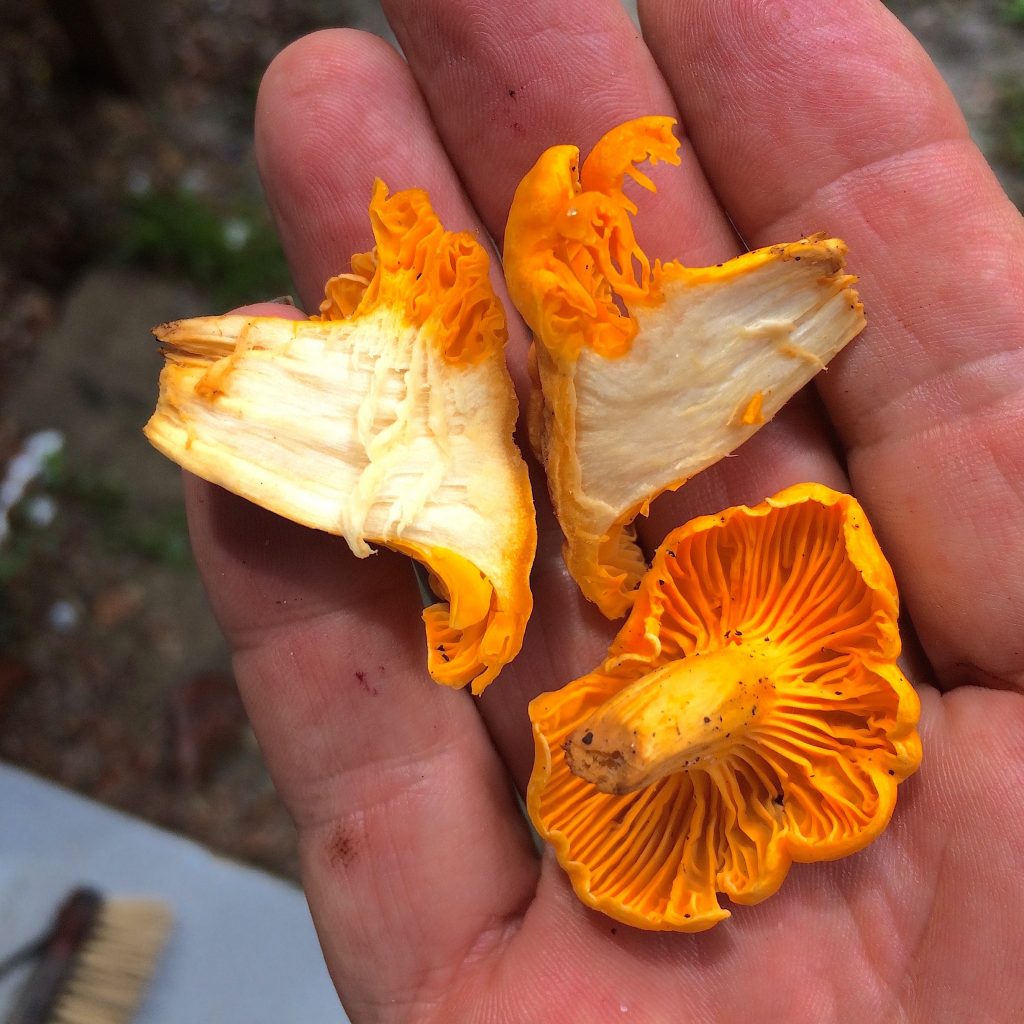

Perhaps the most coveted wild mushroom locally is the Chanterelle. We have several species and sometimes they are difficult to sort out. That is not just in the field. The genus is, as they say, is under revision and the names are changing. Experts can’t agree exactly how many species there are and how many of them are found locally. It’s fairly easy to tell if one has a Chanterelle. It’s a bit more of a challenge to figure out which Chanterelle you have. I collected some 22 pounds of them last year. They are distinct enough in flavor and texture to hold their own in recipes. I like them sautéed with scrambled eggs.
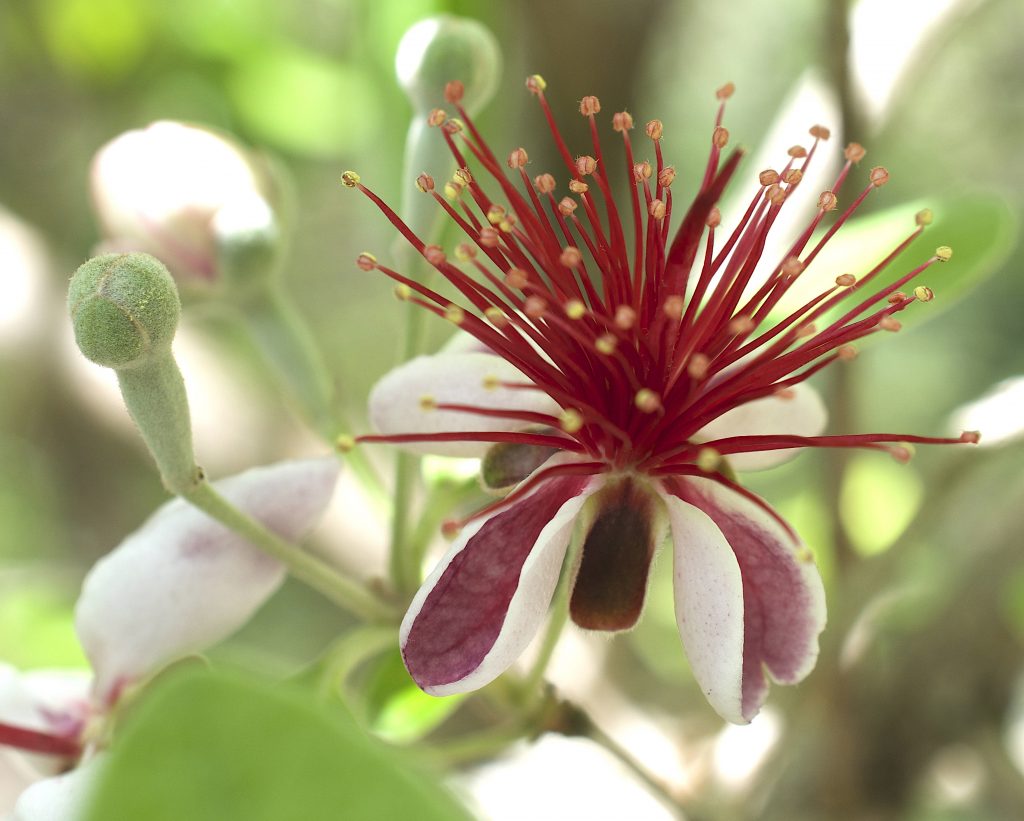

Perhaps no ornamental was championed as much as the Pineapple Guava. However the perfect shrub for many places never really caught on. There could be several reasons for that. It probably didn’t help that a close relative, the Strawberry Guava, is a severe invasive species in some locations. The shrub also does not get showy. It’s almost always drab. And while the blossoms are extroverted you have to hunt for them. While the entire blossom is edible most people only eat the petals. Five or six months from now they will be dark green fruit that stay green as they ripen. They just get softer. The shrub is easy to identify when in blossom. To read more about both guavas, go here.

Let us revisit what is blossoming this time of year: The Eastern Coral Bean. It is also sometimes called the Cherokee Bean. What is odd about this plant is the edible flowers produce toxic beans. So we do not eat the red and black beans. A few of the red blossoms are edible raw but they are usually boiled then mixed with other foods notably scrambled eggs. When you cook the blossoms they turn light green. The distinctive shape of the leaves makes the shrub easy to identify. Young leaves are edible cooked but are marginal fare. Like the Pawpaws above they prefer dry, sunny places. A few raw red blossoms seem okay but if eaten in larger amounts they can be mind altering and approaching dangerous. Boiled they are fine. (Juice from the shrub’s stems, by the way, has been used to treat scorpion stings.) You can read more about the Eastern Coral Bean here.
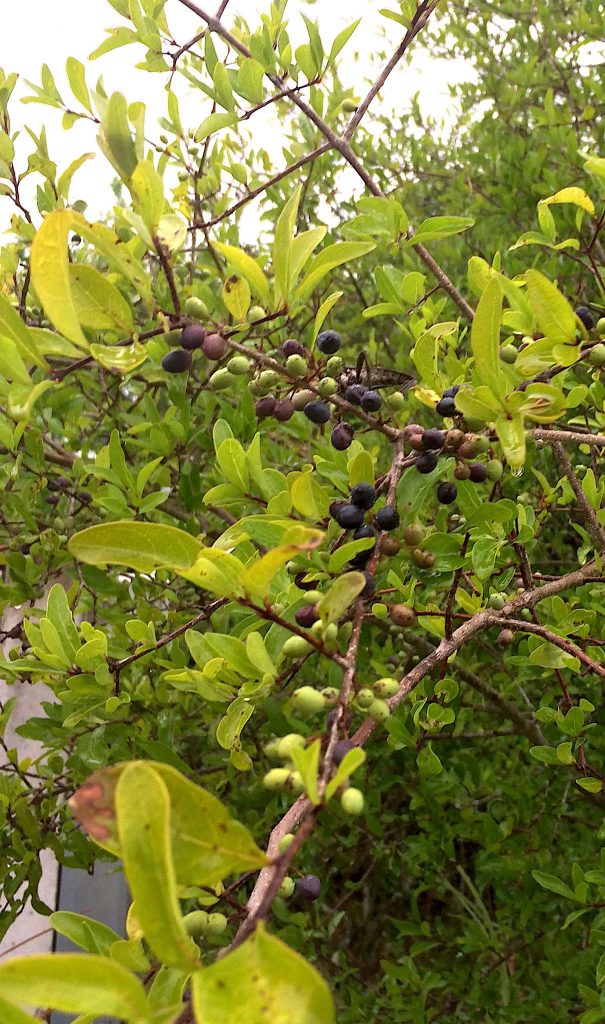

What’s the old saying? Close but no cigar. That might be the case with Foresteria segregata. Also called Florida Privet and Swamp Privet, you can find it anywhere from brackish waterways to an intentional ornamental in landscaping. The straight limbs were used for arrows and the blue berries possibly used for ink. I suspect the species has never worked its way into ethnobotanical literature because the berries taste bad. I’m not sure, however, if the story ends there. Yes, the berries are not considered edible. That said I have not found any references to toxicity but that might be because they are too foul to eat. However, it is in the Olive family and olives don’t taste good unless “cured.” What I wonder is 1) if the fruit are edible if 2) they are treated (meaning cured) like olives? It’s pure speculation on my part. They could be toxic for all I know. But it’s an idea.

Foraging classes: Saturday’s class is in my own backyard, so to speak, Orlando, Blanchard Park. The rain should be past but it might be a little chilly. Sunday’s class is in Eagle Park Lake in Largo, a site we haven’t visited for several months.
Saturday, April 20th, Blanchard Park, 10501 Jay Blanchard Trail, Orlando, FL 32817. 9 a.m. to noon. Meet next to the tennis courts by the YMCA building.
Sunday, April 21st, Eagle Park Lake, 1800 Keene Road, Largo, FL 33771. 9 a.m. to noon. Meet at the pavilion near the dog park. Arrive earlier than later as it is Easter and the park can fill fast.
Saturday, April 27th, Red Bug Slough Beneva Road, Sarasota, FL, 34233. 9 a.m. to noon. Meet at the parking lot.
Saturday, May 4th, Colby-Alderman Park: 1099 Massachusetts Street, Cassadaga. Fla. 32706. 9 a.m. to noon. Meet by the bathrooms.
Sunday, May 5th: Ft. Meade Outdoor Recreation Area, 1639 Frostproof Highway, Fort Meade, FL 33841. (Frostproof Highway is also Route 98.) 9 a.m to noon. Meet at the brown bathrooms in the middle of the park which is due south from the highway.
Saturday, May 11th, Dreher Park, 1200 Southern Blvd., West Palm Beach, 33405. 9 a.m to noon. Meet just north of the science center in the north section of the park.
Sunday, May 12th, Lake Woodruff National Wildlife Refuge, 2045 Mud Lake Road, DeLeon Springs, FL. 9 a.m. to noon. A few hundred feet after crossing the railroad tracks on Mudlake Road there in the parking lot on your right. We meet there. This is a hike of approximately four miles, two out and back mostly native species, very few ornamentals. While the walking is easy we are exposed to the elements, sun on a clear day, wind on a cold day. Check the weather, dress appropriately. Bring water, wear suitable footwear. Know that as it is federal land it can be closed anytime for any reason without notice.
Saturday, May 18th, Florida State College, south campus, 11901 Beach Blvd., Jacksonville, 32246. 9 a.m. to noon. We will meet at building “D” next to the administration parking lot.
Sunday, May 19th, Boulware Springs Park, 3420 SE 15th St., Gainesville, FL 32641. 9 a.m. to noon. Meet at the picnic tables next to the pump house.
For more information or to sign up for a class go here.
Foraging is more than identifying edible wild plants. It also involves knowing how to cook them, when they are prime to harvest, and subject of this review, where to find them. In real estate the mantra is “location, location, location.” We could use that with plants but a refinement would be “environment, environment, environment.”

We know not to look for swamp plants in a desert, unless there is an isolated spring there such as an oasis. Likewise, few cactus grow in swamps though there are exceptions. We also usually find salt tolerant plants near the shore or inland near salt licks (and sometimes along northern roads salted every winter.) But some of those salt-tolerant plants will grow in your garden and do not need to be in a salty environment. Sea Purslane is found on the shore or near brackish water where its job is to build soil by forcing the wind to slow down and drop sand. But, it will also grow in your garden, no salt or wind needed. Other plants are more picky and won’t grow well if not in their preferred location.

For example, one species I am long-familiar with is Blueberries. They like soil on the acidic side, a pH below 7 on a 14-point scale. I grew up in poor-soil Maine where one could find 120-acre fields of nothing but Blueberries. Yet where I live in Florida Blueberries are found in small colonies in isolated pockets. Why? One answer is Florida is a limestone plate (alkaline not acidic) so it is a waste of time to look for Blueberries unless there are acid-producing pines, oaks or perhaps cypress nearby. I planted Blueberries specifically bred for Florida but one has to amend the soil — the amount of acid — nearly as much as one has to work daily to keep a pool from turning green. They eventually died, one of my few failures.

Another example is Dandelions. I have observed for several decades that Dandelions don’t like Florida, or at least the areas of Florida I visit. They like acidic soil. It might be it is not Florida’s heat they don’t like but rather the alkaline (“sweet”) soil. The few places I have seen Dandelions growing have been areas of acidic soil again near pines and often oaks. Dreher Park in West Palm Beach is a good example. What Dandelions there are there can be found growing in lawn grass amongst oaks. While I have also found Dandelions year round they tend to favor the winter months such as November through February.

Some plants can do well in nearly any soil. Henbit, Dead Nettle and Shepard’s Purse are good examples. However, a close relative of Shepard’s Purse, Poor Man’s Pepper Grass, likes soil on the alkaline side. This means you probably won’t find Pepper Grass near Pines and Oaks. Plants that like acidic soil (below a pH of 7.0) that you can find near Oaks and Pines include Eastern Bracken Fern, Curly Dock, Mullein, Nettles, Violets, Pineapple Weed, Plantagos, Wild Radish, Sheep Sorrel, Sow Thistle, and wild Strawberries. Plants that like it on the “sweet” or alkaline side besides Pepper Grass? Wild Carrots, Lamb’s Quarters, Amaranth, Pokeweed, White Mustard, and Purslane. Don’t look for those in an oak scrub or with a lot pines around.

Besides the pH of soil the kind of soil can make a difference. Chicory likes “heavy” soil meaning lots of clay, or rocks. Also liking heavy soil is Broadleaf Dock, Daisies, Milkweed, Plantains, true Thistles, and Wild Garlic. Plants that can endure hard packed soil include Field Mustard, Morning Glories — some of which are edible — and Pineapple Weed (it used to grow in our gravel driveway.) Going the other directions, plants that like sandy soil include Goldenrods, Sandspurs , Horsemint, and Spurge Nettle. Plants too look for in agricultural soil include chickweed, Dandelions, Lambs Quarters, Plantains, Amaranth and Purslane. And while Florida Betony can grow edible roots in rich loam or sand it tends to grow larger and easier to harvest roots in sand.

By their very presence some plants can tell you about what’s in or not in the soil. Burdock likes soil very high in iron and sulfate but low in calcium and manganese. Chickweed and Dandelions like low-calcium low-phosphorus soils. Crabgrass likes very low levels of calcium, phosphorus but high levels of chlorine, magnesium and potassium. Oxalis and Hop Cover, however, prefer low levels of calcium but high levels of magnesium. Purslane and Mustard like high phosphorus levels.

If you see a healthy patch of White Clover you know the soil is lacking in nitrogen. Or said another way, you won’t find happy White Clover in nitrogen-rich soil. I suspect that holds true for other members of the pea family as well. Because of preferences you will usually not find amaranth and clover growing together. Red Clover, however, prefers to grow in areas of soil high in potassium. Wild Garlic also likes high potassium as well along with chlorine, magnesium, and sodium.

All My Videos are available for free on You Tube. They do have ads on them so every time you watch a Green Deane video I get a quarter of one cent. Four views, one cent. Not exactly a large money-maker but it helps pays for this newsletter. If you want to see the videos without ads and some in slightly better quality you can order the DVD set. It is nine DVDs with 15 videos on each for a total of 135 videos. Many people want their own copy of the videos or they have a slow service and its easier to order then to watch them on-line. The DVDs make a good gift for that forager you know especially as spring is … springing. Individual DVDs can also be ordered or you can pick and choose. You can order them by clicking on the button on the top right hand side of this page (if your window is open wide enough.) Or you can go here.
Want to identify a plant? Looking for a foraging reference? Do you have a UFO, an Unidentified Flowering Object you want identified? On the Green Deane Forum we chat about foraging all year. And it’s not just about warm-weather plants or just North American flora. Many nations around the world share common weeds so there’s a lot to talk about. There’s also more than weeds. The reference section has information for foraging around the world. There are also articles on food preservation, and forgotten skills from making bows to fermenting food. One special section is “From the Frightening Mail Bag” where we learn from people who eat first then ask questions later. You can join the forum by clicking on “forum” in the menu.

Donations to upgrade EatTheWeeds.com have gone well. Thank you to all who have contributed to either via the Go Fund Me link, the PayPal donation link or by writing to Green Deane POB 941793 Maitland FL, 32794.
This is weekly issue 351.

