I have written extensively on this site about edible flowers, both cultivated and wild. Here 103 previous separate entries about wild flowers are in one spot. So if it seems you have read parts of this before, you might have. However, this focus is just on wild flowers.

Wild Garlic putting on cloves
The author of “Florida’s Incredible Wild Edibles” Dick Deuerling, now in his 90s, taught me several decades ago that: If it looks like a garlic and smells like a garlic it is a garlic and you can eat it. If it looks like an onion and smells like an onion you can eat it. They must have both, however, look and aroma. We have a lily here in Florida, for example, that looks like an onion but no aroma, and raw it can be deadly. Look and aroma, like horse and carriage and love and marriage. Together. Alliums can also be deceptive. Locally the “wild onions” (read really garlics) grow their cloves on the top of the plant, not underground. And if I remember correctly, an onion always has a singular bulb per plant where as the garlic as sectioned cloves. At any rate there are some 400 species if you include onions, garlic, chives, shallots, and closely related ramps/leeks, the latter having wide leaves. Usually the flowers have a stronger flavor than the leafy parts, and the developing seed head even stronger flavor. Blossoms are usually white but can also be pink. Onion stems are round, as are chives but smaller. Garlic leaves are flat.

Alpine Cress
As the name suggests, you have to go up to find Alpine Cress. It’s no flatland flower, and also as the name suggests, it is in the greater mustard muster. Alpine Cress, Arabis alpina, grows in the mountainous areas of Europe, north Africa, eastern Asia, and the Isle of Skye (Cuillin Ridge.) It is also found in North America including Kentucky, Virginia, West Virgina, Wisconsin, Michigan, New York, Maine, most of Canada, and Greenland, hardy little soul that it is. It likes to grow in damp gravel and screes. Not surprisingly it can be found in many places intentionally planted in rock gardens. The young leaves and flowers are a good substitute for cress. They are edible raw or cooked and are often mixed with other greens as a flavoring.

Alyssum
Mat-forming Alyssums recently underwent a genus and species name change. They were Allyssum lobularia and now they are Lobularia maritima. A native of the Mediterranean areas it has traveled far and is found 41 states most of Canada.The genus name lobularia comes from dead Latin and means small globe, referring to the shape of the flower cluster. Maritima refers to its habitat, meaning it likes to grow near the seashore and is somewhat salt tolerant. . Leaves, young stems, and flowers are used for flavoring in salads or any dish where pungency is desired. The flowers candy well. The blossom are honey-scented.

It’s difficult to imagine a kitchen or herbal medicine cabinet without Angelica around someplace. Angelica has long been valued for its seeds, stems, leaves and shoots. The first two for flavoring — such as in Chartreuse — and second pair as cooked greens, particularly in the Izu Islands of Japan where there are a favored addition to springtime tempura. They have a celery-like flavor. North American Indians, however, smoked the leaves for medicinal purposes. Celery-ish may its green parts be the blossoms, however, have a light anise flavor. Don’t confuse the blossom with Poison Hemlock or you will be seeing angels not angelica.

Apple Blossom, eat only a few
Every seed in every Apple is different than the parent apple trees. Every apple you eat of the same kind is a clone because there was only one original apple tree with that apple. That’s how there came to be some 7,000 different kinds of apples over the years. With mechanization that number has about half. Around the home I grew up in were many wild apples of no distinct variety, just something that sprouted from a tossed away core. Each one unique. What most folks don’t know is that you can eat apple blossoms. Soft scented, floral, only consume a few at a time because they contain a precursor to cyanide which gets release during digestion. A little is tasty. Too many is a tummy ache. A lot is a trip to the hospital.

Basswood Blossom
My first association of the Basswood tree was not with flowers but its soft young stems. My father used to make home wood pipes out of apple wood then use a basswood stem for the pipe stem. If the cattail is the supermarket of the swamp the Basswood tree is the supermarket of the forest. Read about it in another article. However, its blossom are edible and make a well-known tea though you may know of it by its other name, Linden tree and Linden tea. The Linden tree is nearly impossible to misidentify in that it is the only one in North America that has what looks like a large tongue depressor under the blossom. The flowers are delicate and have a honey flavor.

Bee Balm
Bee Balm is another huge selection of flowers closely related to the mint family, in this case Monarda punctata. Intense, aromatic, the flavors can vary not only species to species but between cultivated specimens and their wild siblings. The leaves are often used to make tea, some with calming qualities. Often the entire plant is placed in the house to give a pleasant aroma as it dries. The blossoms tend to reflect the flavor of the parent plant but usually have hints of oregano to thyme to citrus flavors.

Paper Birch Catkins
There are several advantages to living where it never snows, and a few disadvantages. Many plants need cooler weather to reproduce or fruit or just thrive. Birches do not like Florida though they can be planted in the norther bounds of the state. Birches were a common tree of my youth, white birch, golden birch and paper birch. Birches can be tapped like maples. The twigs and catkins have been used as a wintergreen-ish flavoring for as long as we have written records about North America. And of course there were the famous birch bark canoes. What you also might not know is that an epoxy-like tar can be extracted from birchwood. The original super gule. While most birches have edible parts we are interested in this article in the Paper Birch, Betula papyrifera. Very young leaves, shoots and catkins can be eaten in salads or stirfried. The sap makes a drink, a syrup or a sugar, depending upon how long you heat it up. It can also be used to make brich beer and vinegar. A tea can be made from the leaves and the wood used to smoke meat.

Bitter Gourd Blossom
The Bitter Gourd, Momordica charantia, will never with a popularity contest with most people. Though it is a plant that serves us well with many parts edible and medicinal uses it also is bitter and smells like an old, wet, rubber gym shoe. Not exactly a match made in botanical heaven. The leaves can be cooked as a green, and the water used as a tea that controls blood glucose. The bitter fruit is edible cooked and red arils around the seed –the arils not the seed — are edible and nearly all lycopene. And the fragrant blossoms can be used for flavoring.

Black Locust
No accounting of edible wild flowers would be inclusive without mentioning the Black Locust, Robinia pseudoacacia. Just about the entire tree is useful in some way including the flowers. Fragrant, they are made into fritters in America, Europe and Asia. For a tree native to the Southeastern US it gets around. The white flowers are also made into tea. Incidentally, the pink flowers of the Robinia neomexicana are also edible. The Black Locust is sometimes called the False Acacia, which is what its species name means in dead Latin. Planted in France, it is the source of that country’s Acacia Monofloral Honey. It actually produces more honey than the Honey Locust.

Blue Porterweed
I do believe I was the first to publish anywhere in modern times, Internet or otherwise, that Blue Porterweed blossoms are edible. Even the venerated Cornucopia II doesn’t mention it. No doubt their edibility was known long ago because the flower has been used for at least a few hundred years to make tea, beer and as a flavoring. I am sure somewhere along the way someone tried the flowers. Locally we have two versions, a native which grows low, and a tall cultivated one. The flowers on both are edible, and the odd part is they taste like raw mushrooms. As with many delicate flavors the nose is quite involved and it takes a few moments for the flavor to come through. Tasters find it amazing. The flavor does not survive cooking. Incidentally, the leaves are used to make a tea and beer and the stem is used for flavoring.

Blueweed
Closely related to borage and Italian Bugloss, Blueweed, Echium vulgare, is naturalized througout most of North America, missing only from Florida, Mississippi, Alabama, North Dakota, Arizona, Nevada, California, Canada’s Northwest Territory and the Yukon. A native or Europe, it’s an invasive species in Washington state. What is slightly odd about Blueweed is that the blossoms start out pink and turn blue. However, the stamens remain red making the blossom striking. Echium is grown as an oilseed crop and contains significant amounts of gamma linolenic acid (GLA) and the rarer stearidonic acid. Leaves are cooked and used like spinach. The flowers are candied and added to salads. The plant is covered with spines, so pick carefully.

Caesar Weed
There are many invasive species plants locally, some of them intentionally introduced by the United States Department of Agriculture. One of them is Caesar Weed, aka Caesarweed and Caesar’s Weed, botanically Urena lobata. It was brought to the state as an industry to make fiber and indeed in Africa they still make burlap out of Caesarweed. They ret it like flax, which is to soak it in (preferably) running water which causes the fibers to separate. Young leaves are edible cooked but they are a famine food as they never loose their sandpaper texture. There is a separate article about them on site. Caesarweed is in the mallow family and produces a small, pink mallow blossom which can be eaten raw. Toss it into salads.

Immature Cattail Blossom
You many not think of a Cattail as having a blossom but it does and before it matures it is edible. In fact, both the male part of the flower and the female part of the flower are edible. Later when the male part produces pollen that’s edible as well. When the female parts turn brown it’s way past edible. The male part is the spike on top, the female part the wider portion below the spike. When both are green they can be boiled. The rest of the plant has edibles as well and is a well-know staple of the forager. The cattail rhizome is full of starch. In fact, no plants produces more edible starch per acre than the cattail.

Sprinkle chickweed blossoms on a salad.
Chickweed, Stellaria, is not a blossom that comes to mind when one things of edible blossoms because one rarely separates the small blossoms from the rest of the chickweed before it becomes food. However, the deeply-lobed tiny five-petaled blossoms can be separated and sprinkled like white snow upon salads. Admittedly this is more for effect but isn’t that part of why we eat pretty flowers anyway? Also note the Native Americans did not let the weed’s small size deter them. They also used the minute seeds to make bread or to thicken soups. And of course, the rest of the chick weed above ground can be used as a potherb. It can be eaten raw if you like the flavor of corn silk. Some folks just toss everything into a blender and make a green drink out of it

Chicory
I can remember the first time I saw Chicory in blossom, or ever for that matter. I was in Alexandria, Virgina, visiting a dear friend for a couple of weeks and wandering amongst parks, monuments, and museums. The mower had somehow missed it and I noticed it immediately. The blue pretty Chicory is a close relative of the dandelion but not sweet at all, In fact it runs towards bitter and earthy. Think radicchio. You can eat the flowers and the bud, or pickle the buds. The root has been roasted and used to extend and flavor coffee.

Citron Melon
The two plants non-foraging people ask about all the time are Society Garlic (covered elsewhere) and those small watermelon like fruit seen in old citrus groves and abandoned fields. The short answer is they are Citron Melons. They used to be cultivated for to make preserves and I have a separate article on them. However, their blossoms are edible if they are not bitter and you remove the pistils. The blossoms should be cooked though usually one never sees the plant until the late fall and winter when one can see the fruit from the seasonal die back. The blossom might be edible raw, I just haven’t tired them. Seminole Pumpkin blossoms can be used the same way. Again remove the pistils.
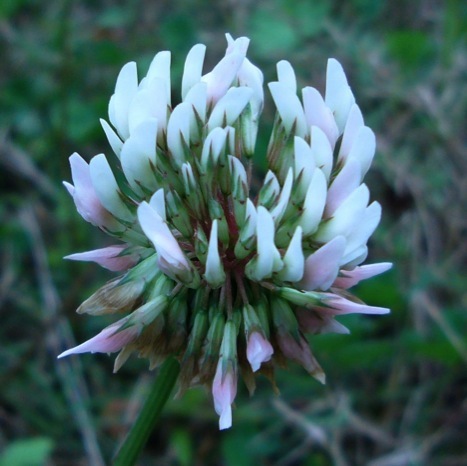

My mother told me there wasn’t a time when she couldn’t remember not eating white Clover blossoms, Trifolium repens. That’s interesting because raw clover blossoms aren’t the easiest to digest. In fact, the entire clover family is on the cusp of edible not edible. It’s high in protein and the flavor of the blossoms is alright but eating clover leaves is more on the famine food side of life. As for the blossoms, they are usually made into tea which brings a precaution. This is usually about sweet clover but should be remembered for all clover. They should be used totally fresh or totally dried, not wilted and never moldy. In fact, moldy clover is how they discovered the “blood thinner” coumadin, read after it killed a lot of cows. So when you use clover, particularly sweet clover, make sure it is either totally fresh, or totally dried and has no mold. And yes, you can eat red clover blossoms, too. Sweet but on the hay side.

Coltsfoot
Coltsfoot has become controversial. Young leaves, flower buds, and young flowers can be use in soups or as potherbs. Fresh or dried flowers are used to make an aromatic tea. A delicious wine is made from the blossoms and ashes from the plant are a salt substitute. Used for centuries it has come under scrutiny for chemical that might cause liver damage, at least in infants. There is one documented case of coltsfoot tea causing severe liver problems in one infant. In another case, an infant developed liver disease and died because the mother drank tea containing coltsfoot during her pregnancy. The plant has also been used for centuries to make a cough suppressant. Indeed, its botanical name Tussilago farfara means “cough suppressing activity.” A European native it is naturalized in the northeast quadrant of North America as well as Washington State and British Columbia.

Common Mallow Blossom
How many names does this mallow have? There’s Common Mallow, High Mallow, Tall mallow, Mauve des Bois, Cheeses, and botanically Malva Sylvestris, which means mallow of the woods. Native to western Europe as the plant moved with colonialists it picked up various names. It’s an annual in cool areas and a perennial in warmer areas. It is found in most states save the Old South and Nevada though it does grow in South Carolina. the mucilaginous leaves are eaten like spinach, added to soups to give them texture, or used to make a tea. Flowers are used like a vegetable or as a garnish. Unripe fruits are called cheese because they look like a small wheel of cheese. They are a nibble. Look for blossoms from June to September.

Tansy’s Rayless Blossoms
Another escapee from Eurasia now found over most of North America and the rest of the world is the Common Tansy. First mentioned for medicinal uses by the Ancient Greeks, the “bitter buttons” by the 8th century were in Charlemagne’s herb gardens and used by Benedictine monks in Switzerland. In 16th century England it was a “necessary of the garden.” Tansy, related to the thistle, even been used as an insect repellent. In fact, meat (and corpses) were wrapped in it for preservation and keep insects at bay. It is not a good repellent against mosquitoes but does a good job with the Colorado Potato Beetle. Like chamomile it contains thujone so it should be used sparingly. But then again, that’s what spices are for. The blossoms’s flavor is bitter, camphor-like.

Coral Vine Blossoms Must be Cooked
The Coral Vine has dozens of names, not only as a cultivated blossom but an escapee on the most noxious list. Botanically it is Antigonon leptopus. A native of Mexico it has edible roots, leaves and for this series, flowers. To read more about it see a separate entry on this site. The vine can climb to some 40 feet and blossoms nearly year round in warm area. Butterflies and bees like it (you’ve been warned) because over 40% of its blossoms are open at a time. The blossoms, like the leaves and roots, have to be cooked.

Corn Poppy
They used to be far more common than they are now, paper red poppies around Veterans Day, sold to raise money for disable veterans and the like. Aside from the veteran connection, mention Poppy and opium is usually the next topic mentioned. That’s a different poppy so hold the email please. Our poppy is Papaver rhoeas, common name is Corn Poppy, sometimes Flanders Poppy. From Athens Greece to Athens Georgia, you can find Corn Poppies. In fact, they are the flower of profusion about the Agora down from the Acropolis. Young leaves are cooked and seasoned like spinach, or used for flavoring in everything from soup to salad. Syrup is made from the red petals is used to add flavor and color soups as well as wine. The seeds are used in confections and bread and the oil is an excellent substitute for Olive Oil. Originally from Eurasia they are found in most areas of North America.

Cow Slips Blossoms
My mother’s mother loved Cow Slip greens. Cow slip is from the old English word “cuslyppe” which means cow dung. Apparently the species has the same feeding preferences as some famous mushrooms. So my grandmother would make my mother go out in the cow-containing pastures to pick the cow slip greens. And from the way my mother tells the tale my grandmother didn’t care whose pasture she spied the plants in. They were destined for consumption after my mother fetched them. From temperate Europe and Asia originally, Cow Slip, Primula veris, is in the same genus as the (English) Primrose mentioned earlier. Flowers are used in salads, conserves, or as pickles and a garnish. They have also been used to make cow slip wine and vinegar. Leaves are eaten raw in salads or used to make a tea. It is found in northeastern North America.

Golden Currants
We used to ride our horses on abandoned roads, of which there were plenty. One was still passable if you had a vehicle with a high suspension because the road went over washed out ledge. It was no problem for the horses. At the top of the ledge were high bush blueberries, some eight feet tall. Just beyond the crest were two fallen-in farms, across the road from each other which usually meant the same family. Still growing at one of the homesteads was Currants. Currants, gooseberries and Kiwis are related to each other. Currants were made into jellies and jams as well as wine… very good wine. The natives dried them and use them in making pemmican. Some species, perhaps most, have edible flowers. At the top of the flower list is Ribes aureum, or Golden Currant, found in most of North America except the Old South. Another currant noted for flower edibility is Ribes cereum. Wax Currant, found in the western half of North America. Black Currant (Ribes nigrum) flower buds are used in ice cream and liqueurs. I would suspect the open flowers would be usable as well. And of course, the berries have many uses and have antioxidants. Incidentally, R. aureum is not Ribes odorata.

Daisy
If I remember correctly Jean Kerr titled one of her humorous books, “Please Don’t Eat The Daisies.” The Daisy was Bellis perennis, or the English Daisy but now just called Daisy as it is the common flower of farm and field in North America, and South America. For a widespread plant in multiple uses it is not high on the flavor list, if not bitter. However, its leaves have been used as a cooked green, usually boiled or as a pot herb. Flower petals are eaten in salads, remember bitter. Flower buds are eaten in sandwiches, soups and stews, or pickled and used like capers. The entire flower open in the day and closes at night. “Daisy” is from Day’s Eye, meaning open only during the day. And, while it looks just a center blossom with a lot of rays around it, each ray is a separate flower, and every tiny yellow section in the middle is a separate flower.

Dame’s Rocket is a Mustard
Dame’s Rocket is a declared invasive species in several places. It’s your civic duty eat the weed. Originally from Eurasia some 400 years ago it’s a mustard that at first glance looks like Phlox. Dame’s Rocket has the typical mustard family four petals, Phlox, five. It’s found essentially everywhere in North America except the Old South. Botanically known as Hesperis matronalis, it is cultivated, escaped and is included in wild bird seed mix. Young leave collected before flowering are eaten like cress. Seed pods can be added stews and soups. Seeds are a source of oil and can be sprouted and eaten. The flowers are used to add spicy flavors to fruit dishes and salads.

Dandelion’s Cheery Rays
Perhaps no wild flower is better known as edible, or played with, than the Dandelion. Who hasn’t sent the flower’s powder puff of seeds off into the wind with a strategic breath of air? The first batch of wine I made as a kid, after two successful crocks of beer with cooking malt and bread yeast, was dandelion wine. The yellow parts of the blossom are sweet, if not honey-flavored. It makes a fine homemade wine and the blossom added to salads (or pancakes) is a cheery compliment. However, trim off all green parts unless you happen to like bitter. And with all wild plants, be careful where you harvest to avoid pollution.

Dayflower, a Commelina
My love affair with Dayflowers is over. They don’t like me anymore. Well, the raw stems don’t. The raw blossom still do. In the Commelina clan there’s quite a few of them and while the blossoms are fine to toss in a salad, candy or use as a garnish — just like their relative the Spiderworts, I am beginning to think the stems and older leaves are overrated. Raw, they irritate my tummy these days. I have an article on them on site. The blossoms can vary in size depending on which species and can have three blue petals, two blue petals and one small white petal or two large blue petals and one smaller blue petal. Their flavor is an inoffensive green. The Yellow Commelina, Commelina africana, is also edible cooked.

The original Daylily
A foraging standby in all but the southwest desert and northwest Canada is the Daylily. But first a couple of precautions. I am talking about only the Hemerocallis genus. Also go sparingly, they can be diuretic or laxative. That said day lilies are on the sweet side, vegetable-ish. Like squash and glad blossom they’re used to hold tasty finger food but like other blossoms cut them away from the white bitter base. I used to enjoy them often but the only local patch is now under a highway exit. See full article on site and video.

Eastern Coral Bean
Like the Eastern Redbud below the Eastern Coral Bean is a seasonal treat. Unmistakable in the springtime it sends up a flower spike populated with red, tubular flowers. The plant has hummingbirds in mind. Flowers ripen for a few weeks then turn into toxic berries, which we do not eat. While the blossoms can be eaten raw they are usually cooked first by boiling. When you do the loose their color and turn light green. Slightly beanish, their traditional use is to mix in with scrambled eggs. Other species such as the Western Coral Bean are in similar ways, and also usually cooked. See full article on site and video. Erythrina american blossoms are used in a similar way.

Eastern Redbud
In the spring time in North America if you see a tree with no leaves and small pink blossoms it is almost certainly the native Eastern Redbud. I say almost certainly because here in Florida there is an imported ornamental that does the same thing at the same time with pink blossoms, except they are huge whereas the Eastern Redbud’s blossoms are small. Native Americans ate redbud flowers raw or cooked as well as the young pods and seeds raw or cooked. The flowers can be pickled. They have a slightly sour taste and are high in Vitamin C . They’re a pleasant addition to salads and can also be used as a condiment. The unopened buds can be pickled or used as a caper substitute. See full article on site and video. Cercis siliquastrum can be used the same way.

“Elder Blow”
No compendium of edible wild flowers is complete without mentioning Elderberry blossoms. Small, aromatic, they have been used for tea at least for centuries with some recipes 600 years old. They can also be put into pancake batter and the like to sweeten and give a nice texture. Another use for the blossoms is to flavor a light summer time sparkling wine, or as my friend Dick Deuerling would call it “Elder Blow Champagne.” The dark purple to black berries have been used medicinally — particularly for colds and flu — and in the kitchen. I like Elderberry pie and to use the dried berries as a spice such as on ham.

Eucalyptus Blossom
While on the topic of flowers that are not edible but produce a sweet nectar than let’s add the huge family of Eucalyptus. Here in North America Eucalyptus is usually thought of in medicinal terms, some what in the same category as camphor, one of those aromas in your grand- or great grandmother’s house. Where they are native however, Eucalyptus are significant producers of honey, flower nectar, and “manna” sweet dripping directly from the tree or scraped from leaves. Cornucopia II lists no less than 37 Eucalyptus species producing, honey, nectar, manna and in come cases edible bark and seeds. “Eucalyptus” comes from Greek. “Eu” means “well” and “kaleptos” means covered. Well-covered, in reference to the hidden flowers. The base of flowers are sipped on for their nectar. Incidentally in Greek Eucalyptus is pronounced eff-KA-lip-tos. Blame the difference on Dead Latin.

Everning Primrose, Oenothera biennis
Every climate has its good and bad points and one of the bad points locally is that the tall, northern Evening Primrose does not grow here. I think the the most amazing specimen I ever saw was in Vathia, Greece. It was at least six feet tall and totally covered with flowers. Here in Florida we have a very scraggly ground hugging one. I have not tired its flowers. On my list of things to do. However, the common Evening Primrose of northern climes does have edible blossoms. They are sweet and can be used in a variety of ways raw or cooked if you prefer, salad to soups to garnish. They can even be pickled.

Forest Lily
Closely related to some species in Edible Flowers: Part 18 is the Forest Lily, Veltheimina bracteata. A native to Africa it is found in flower gardens in warmer climates around the world. The species is named for the German patron of botany, August Ferdinand Graf von Veltheim (1741-1801). There are only two species in the genus. The Forest Lily’s inflorescence is a dense raceme of tubular flowers on a long stalk. The color of the flowers vary from pale pink to dusky pink to orange-pink or deep rose pink, occasionally greenish-yellow. The tips of the flowers are sometimes green or spotted with green. Forest lilies flower during late winter to spring. Each flower-head lasts about a month. They are eaten like spinach.

Fragrant Water Lilly
One of the more difficult things about the Nymphaea odorata is what common name to call it. Fragrant Water Lilly and American White Water Lilly seem to be in the running. We’ll go with Fragrant Water Lilly, and it is! Actually the unopened flower buds can be collected and boiled as a vegetable. Once opened the raw blossom can be used as a garnish or nibble. Whether the plant’s rhizome is useful is something of a debate. Some think our local native Nymphaea mexicana can be used the same way.

Golden Alexanders
While the name is pretty and flower is well most folks don’t know about Golden Alexanders, or Zizia aurea. In the carrot family it is a prime edible found in the eastern two thirds of North America plus one county in southeastern Wyoming. It’s native and prefers moist woodlands but is also well-known for surviving droughts. Golden Alexanders blooms from May to June, which varies a bit from Florida to Canada. The yellow flowers are bunched at the top of the plant. Each flower is tiny, some three millimeters long with five sepals, five petals, and five stamens. In the fall the leaves turn purple. The flower clusters with the main stem removed are added to salads, or they make a delicious cooked vegetable reminiscent of broccoli. In Eurasia a related species, Smyrnium olusatrum, Black Lovage, were cultivated as a vegetable, gradually replaced by celery.

Almond flavored gorse
There is a saying: “When Gorse is out of bloom kissing is out of season.” As Gorse is never out of bloom, that’s the good news. The bad news is that it is cover with thorns… Perhaps the wedding analogy is appropriate. A spray of Gorse was traditionally put in the bridal bouquet as a reminder. Whether that is of kisses or thorns I am not sure. One of the The thorns might also explain why its seeds are mostly distributed by ants. Gorse flowers are a trail side nibble. They can be added to salads, made into tea, or used to flavor wine. Oddly, the blossoms smell slightly of coconut but taste like almonds. The bright flowers have also been used for dye, Easter eggs to clothes.

Gunnison Mariposa
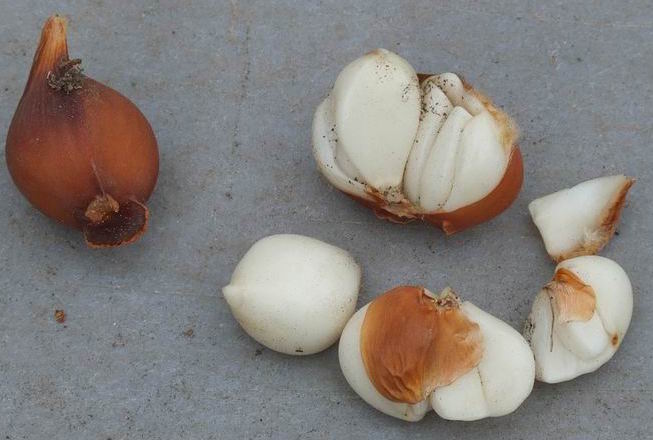
The blossoms of two Mariposa get over looked because so much of the rest of the plants are edible. First the Gunnison Mariposa, Calochortus gunnisonii. The fresh bulbs are easten raw with salt and taste like a raw potato. Fried or baked they have a crisp nut-like texture. Dried they are pounded into flour for use as porridge or mush. The seeds are ground and eaten. And the flowers and buds are eaten raw in salads or as a trail side nibble. The Gunnison Mariposa is found from Mexico to Canada in states bordering or containing the Rocky Mountains.

Hairy Cowpea, Vigna luteola
Hairy cowpeas like water. Not exactly in water but certainly near it, water’s edge. You’ll find them in the same places you find the Ground nut, Apios americana. When you’re near water, fresh or salt, look for pure yellow pea-like blossoms though it’s not really a pea but a bean, and related to the Mung Bean and the Black Eye Pea, which is also a bean. While the Hairy Cowpea, Vigna Luteola, blooms and fruits all year locally it prefers the fall for seed production. It’s usually at that time collecting them is a calorie-positive activity because you can get a lot of the seeds at one time. Of course, the rest of the year is a good time to collect the blossoms and boil them with other potherb fare. The roots can be chewed to extract their sweetness, the seeds can be shelled and cooked and as mentioned the flowers cooked.

Hawthorn Blossoms
When I was growing up I lived on a dirt road out in the country. Across the road, kitty-corner, where two pastures met, was a Hawthorn tree. It was old and large and had two-inch thorns in grand profusion. It was also laden every year with several families of birds because few predators would brave the thorns. As to which Hawthorn tree it was is anybody’s guess, even for a Hawthorn expert. It is one of those genus in which there may be a 100 species or a thousand. It is supposedly a professional joke in the botanical world to send a known Hawthorn to some one rather new and ask them to identify it to which the often reply is it must be a new species. Long ago someone discovered that very young Hawthorn leaves and blossoms in the spring could be eaten together right off the tree, thus the “Bread and Cheese tree” was born. Young leaves can be added to salads or nibble on. The blossoms, which have a peculiar taste, can be added to salads, desserts and drinks. Interestingly old leaves and fruit (minus seeds) are a natural beta blocker for high blood pressure. Two teaspoons of either or mixed ground up in a cup of hot water morning and night is the herbalist’s usual prescription.

Canadian Honewort

High Bush Cranberry
High Bush Cranberries are not cranberries but that’s all right because we are interested in the flower, though the fruit is edible, too. Actually Viburnum trilobum, not a Vaccinium, the High Bush Cranberry favors cooler climates, think the north half of North America, Europe and asia. the blossoms of the High Bush Cranberry is rather odd in that it has sterile large flowers around the outside of the blossom and fertile tiny flowers in the middle. While both types of flowers can be used the larger outside ones are more practical and leave the fertile flowers to make berries. The flowers can be mixed with pancake or muffin batter or can be made into fritters.
The Canadian Honewort, Cryptotaenia canadensis, grows all the way down to Florida, and covers the eastern two third of North America. A member of the carrot family, it can be found growing along streams and creeks or in low, wet ground. The entire plant is edible, cooked, root to flowers. Flowering season is May to August and the blossom are small. Also called Wild Chervil, the roots are usually boiled in salted water and served with oil, young leaves and stems are soaked in water to moderate flavor then cooked as a pot herb. Cooked flowers are edible as well. You can add a small portion to salads for their aromatic quality. Seeds are used for flavoring and the stems candied. Cryptotaenia japonica can be used in a similar way but needs far less cooking, usually just blanching. In warmer areas don’t mistake Tripogandra multiflora for it. The latter has black stems, large flowers, and is not edible.

Hyssopus officinalis
The Hyssop, Hyssopus officinalis, is quite well-known. The leaves and tops of young shoots are used to season soups, salads, pickles, sauces, custards meats, stews and dried for tea. Its bitter-mint oil is used to flavor beer, liquors, and bitters. It is one of the main flavors in Chartreuse. Native to the Mediterranean, it is cultivated globally. What is not often reported is that the blossoms are edible as well, usually added to salads or made into syrup. There are several cultivars. The word Hyssop comes almost diretly form the Greek word ??????? (EEs-so-pos.) It’s naturalized in the northeast quadrant of North America and North Carolina, Colorado, Montana and Saskatchewan.

Indian Paint Brush
While recreating my foraging instructor page for the new website I considered using the state flower next to each separate state entry. Unfortunately few states have state flowers that are edible. Wyoming is the exception. Its state flower is the Indian Paint Brush though it is found in most western states and has a huge variety of common names including — no surprise here — the Wyoming Paintbrush. By statute, however, it is officially Indian Paint Brush. It was adopted as the state flower 31 January 1917 beating out columbine and fringed gentian. There was heated debate, however, from the opponents. One said the Indian Paint Brush was not common in the state, had too many varieties only an expert could tell apart, was parasitic by feeding on the roots of others, wasn’t generally, liked and that the fringe gentian had been already chosen by Wyoming school children as the sentimental favorite. He left out the Indian Paint Brush encourages foraging but no doubt would have if he had known it. This particular paint brush, Castillija linariaefolia, is the best tasting in its genus. Maybe that’s why it won. Flowers are eaten raw. However the plant can accumulate selenium making it toxic to cattle.

Johnny-Jump-Ups
I don’t know if I should tell you about Johnny-Jump-Ups or not. Botanically Viola tricolor, they are among the first flowers I can remember my mother picking from the wild and eating on the spot. She did it because her mother did it (and she also never missed harvesting a cowslip either.) Johnny-Jump-Ups like moisture and can tolerate shade so… here goes…. Our house in the country had a septic system and a drain field. That drain field was moist and shaded and Johnny-Jump-Up grew there in profusion. And that is where my mother picked them, one after another, eating them on the spot. She’s now 86. Johnny-Jump-Ups have a mild wintergreen flavor and a variety of uses. They’re added to salads, desserts, soups, served with cheese and used to decorate confections. Incidentally they are the ancestor of the common Pansy.

King’s Spear
Like many European wild flowers the King’s Spear, aka Asphodel, Asphodeline lutea, is found in flower gardens around the world. These days it is appreciate for its looks more than its flavor. However, the ancient Greek and Romans roasted the roots and ate them like potatoes with oil and salt. Sometimes they mashed them with figs. The flowers are also eaten and have a sweet, delicious flavor. It will grow in any soil and under most conditions except facing north. Very showy, low maintenance, blossoming for about six weeks from May into June. Harvest roots in fall.

Kudzu blossoms smell like grapes
You never have to go looking for Kudzu blossoms. When kudzu is in bloom there is no mistaking its scent. It is smells eactly like the cheap grape bubble gum kids chew. And intenst? You can detected it on the wind from 100 yards away, or more. Kudzu is the bane of the Old South. Introduced by the government which paid farmers to use it for land reclaimation, it can grow a foot a day and covers some 120,000 new acres every year. Goats love to eat it and all of it is edible except the seeds. The blossoms are quite edible recipes abound in their use, jelly to wine. While the smell like grape they do not taste like grape. They are sweet and have a flavor of their own.

Loroco, Fernaldia pandurata
If you like Latin American cuisine one of the well-known edible flowers, buds and blossoms, is the Fernaldia pandurata, or Loroco. It is part of the traditional dish pupusas. It grows wild in northern Central America and southern Mexico but is also under cultivation and will grow in south Florida. The buds and unopened flowers are cooked with cheese, eggs, rice or chicken. They are also used in crepes, tortillas and tamales. The flowers and buds can also be cooked as greens or folded into egg batter. Originally called Quilite, which means “edible herb” the pungent flowers similar to artichokes in flavor are high in calcium, niacin and fiber, but low in calories. Oddly this vine is closely related to toxic members of the dogbane family but tests on the flowers for cardiac glycosides have been negative. The root, however, is used as a poison.

Magnolia grandiflora
Magnolias are one of the iconic trees of not only the South but exported to many non-hard freeze areas of the world. And people have admired the huge magnolia blossoms for a long time. Few folks know the blossoms of the Magnolia grandiflora are edible, however their flavor is intense and they taste similar to how they smell. They are not eaten raw per se. They are pickled. Oddly the practice started in England and you only use the petals, not the entire blossom. What works best is to pickle the petals in a sweet/sour pickle recipe. Then take out one petal, dice it, and use it sparingly as a flavoring in salads. The flavor is strong so go easy. Also, M. grandiflora’s leaf can be used just as M. virginiana’s can as a bay leaf, that is to flavor soups and the like. However, don’t use the entire leaf because it is way too beg. Cut it into smaller pieces when used like a bay leaf.

Mahoe’s Blossoms Change Color
One of the more fascinating flowers in warm climates is that of the Mahoe, or the Sea Hibiscus. In the morning the blossom is yellow but by late afternoon it is red. The working theory is the shrub changes color to appeal to two different groups of pollenators. If one doesn’t get it in the morning, one might in the afternoon. The change in color also increases the amount of antioxidants. It also helps that almost the entire shrub is edible some way. The blossoms, yellow or red, can be eaten raw or cooked. Their flavor is mild. Incidentally, the Portia Tree, aka Seaside Mahoe, can be used the same way.

Melaleuca Blossom
To compete the trio of sweet flowers that are not edible let’s add the Melaleuca, an invasive nightmare in south Florida. The blossoms and leaves of the M. quinquenervia can be used to make a sweet tea. Usually the tea is made from the leaves and the blossom used to sweeten it. Also called the Paper Bark tree is is used to make temporary huts in the outback as well as containers for cooking food. The Melaleuca is the number one invasive plant in Florida. It was introduced in the late 1800s but got a huge boost after the turn of the 20th century from one Dr. John Gifford. It consumes huge amounts of precious water, is very prolific, and very difficult to get rid of. On the other hand, like the Eucalyptus it is also a prime producer of honey.

Manzanita blossom, red beries to follow
Western states often seem to get short-changed in the foraging realm because most of the edible foreign weeds landed on the east coast. They’ve been slowly working their way west for centuries, which from a botanical point of view is a small amount of time. The West, however, has its own wild edibles including the Manzanita of the Arctostaphylos genus. Both Manzanitas and Bearberries are in the same genus. Of the Manzanitas several have flowers worthy of nibbling on including Arctostaphylos glauca, Arctostaphylos manzanita, Arctostaphylos nevadaensis, Arctostaphylos parryana, Arctostaphylos patula, Arctostaphylos pungens, and Arctostaphylos tomentosa. Besides the blossoms, the berries are edible as well.

Marsh Mallow
Yes, at one time marshmallow, the white, sweet sticky stuff you buy in a jar and mix with peanut butter to make a Fluffernutter, once was made from the Marsh Mallow. The commercial product, however, is much different than the original. A native of Europe it has been naturalized in eastern North America for centuries. It was brought here mainly as a medicinal plant, and has many uses still. Nearly the entire plant has something to offer. We are in this article concerned about the flowers. They can be eaten raw or cooked. When cooked they are on the viscous side. Grayish, velvety leaves helps you identify this mallow from its scores of kin.

Mayflower
A rite of spring in the frozen north, or at least the part I lived in as a kid, was to go looking for Mayflowers. Hardy little souls, they would blossom on the side of small Maine mountains and cope with bone-cold nights and reluctant-to-melt patches of snow and ice. They are the first to blossom after the frost leaves. My mother had her favorite haunts for the flowers and we would go clambering amongst boulders and hardwoods for them. Their intoxicating aroma and the fact they are the only green thing growing that time of year makes them easy to find. Epigaea repens, also called Trailing Arbutus, actually have the same aroma as citrus blossoms. Slow growing and in the Heath family they are salad fare but light and delicate. However, in many places they are rare, so pick accordingly. They are also illegal to pick in some places. Check your local laws, or, have no witnesses and eat the evidence.

Maypop
Maypops are edible, and they look great on the plate. As for flavor… well, the entire plant smells like an old gym shoe, the flowers less so. Let’s call it an acquired taste. They are really too insubstantial to cook. In fact, most of the plant above ground is useful. The leaves can be cooked as a green, and the water they were cooked in as a sedative. The green fruit can be sliced and cooked like a green tomato, and the ripe fruit pul[ and seeds can be eaten out of hand or made into a refeeshing, tart drink.

Meadowsweet
What shall we call it? Meadowsweet or Queen of the Meadow? I grew up calling it Meadowsweet so I’ll stick with that. From the old world it is naturalized in the northeast quadrant of North America, New Jersey north as far as you can go and west to Illinois and then as far north as you can go. And for a botanical hiccup, it is also naturalized in one western state, Colorado. We had multiple horses when I was growing up and subsequently hayed in the summer. I remember many times mowing Meadowsweet and smelling its sweet aroma. Scientifically Filipendula ulmaria, it always grew in the damper areas of the fields. The entire plant is used herbally and in the kitchen to flavor this or that. The blossoms are equally sweet and make a pleasant additions to soups and salads or make a tea, one of the few medicinals teas that’s easy to get down.

Mexican Hyssop
The Agastache genus provides a lot of flowers and leaves for salads and teas. At least nine if not ten species have consumer friendly parts. Despite that one of my readers, a teacher, took some blossoms in for a tasting in her mostly Hispanic class and ran brickwall into the administration who viewed anything not from the grocery store as toxic. Pictured here is Agastache mexicana, Mexican Hyssop, which is in the greater mint family. It’s highly areomatic leaves and flowers are used in salads, for flavoring and tea. Other useable Agastache include: Agastache cana, Agastache foeniculum, Agastache neomexicana, Agastache rugusa, Agastache urticifolia, and Agastache anethiodora.

Milkweed Blossom
When I was a kid back in the Dark Ages I was always covered with Milkweed sap, or Asclepias syriaca juice, and it was sticky! The plants grew everywhere and at the time were taller than me. I was always picking blossoms, snapping shoots, tearing apart green pods and later throwing the fluff everywhere. The spongy, cellular structure of the pod was fascinating, and the final seeds so silky. I can still remember seeing butterflies on the Milkweed blossoms. They knew something I did not. There is sweet nectar in the blossoms… kind of. Milkweed blossoms are an acquired taste and to really get the nectar out they have to be long boiled. However, you can eat the blossoms raw.

Milkweed Vine, Morrenia odorata
By looking at the names of this vine and the attitude of the state of Florida one would never suspect most of it is edible including the flowers. It’s called the Milkweed Vine, the Latex Vine, the Strangler Vine, the latter because it tends to climb on trees and cover them. Botanically it is Morrenia odorata and I have a separate article about it on site. Literally from the ground up this plant is edible and the fruit has more Vitamin C than citrus (which fights to get rid of it.) The flowers are very sweet and floral and can be eaten raw. This vine is only found in warm areas. Don’t try confuse it with the cool climate Honeyvine, Cynanchum laeve, which is not edible.

Mimosa Silk Tree, Albizia julibrissin
The Mimosa Silk Tree, Albizia julibrissin, is native to southern and eastern Asia. From there it was carried to Europe by the mid-1700s. Soon after it was introduced to North Carolina by the French botanist Andre Michaux. From there it spread north to New England, down around the Old South west to California and up the west coast, all except the northern plain states. There is a separate article on site. Young leaves are edible cooked or dried to make a tea. The blossoms are edible like a vegetable or crystalized.

Wild Mint, Micromeria brownei
Mint is such a common edible I almost didn’t include it. Also, which one do you use, and do I put it in the cultivated edible lineup or the wild edibles? There’s over 200 genera and some 7,000 species in the mint family. The largest is Salvia with some 900 members. It would be a lot easier if we were talking about Florida Pennyroyal which is a monotypic genus, a family with one member, not thousands. I am going to opt for a local mint as you probably alread know about your local mint. I learned as this mint Micromeria brownei. Now it is Clinopodium brownei. Ahhh… bontany always trying to improve itself. The mint went from Small Flower Parts Brown to Slope Footed Brown. I’m sure you can see the immediate and dramatic nomenclature improvement…. I was also told all those decades ago it had no common name. When the internet was born the aquarium trade starting calling it Creeping Charlie. Later I saw St. John’s Mint… hmmm not too bad as th St. John’s River runs north through the peninsula of Florida. Only recently Florida Water Mint has creeped up, not a name that imspires me as it can be found in much of the Old South… Maybe Old South Mint is in the offering. This little plant can be found anywhere I teach in the warm south near fresh water. In fact it also grows in Interstate medians leaving a mint aroma in the air for days after car accidents careered off the pavement. A one inch part of any of it, blossoms or stem in a cup of hot water makes a miny tea. The entire plant can be used as mint. Warning: It is a strong, no wimpy mint it. Start sparingly until you get your gauge of use.

Musk Hyacinth
Often plants that are wild in Europe are cultivated in North America, making them difficult to classify. The Musk Hyacinth is such a plant. Botanically Muscari neglectum, the Musk Hyacinth has urn-shaped blue blossoms. They are used as flavoring in Europe. The bulbs are also boiled an eaten. Blossoms of the Muscari botryoides (Muscari botryoides ) are picked and that species in naturalized in the eastern United States plus Texas and New Mexico. A close relative, Leopoldia comosa, the Tassel Hyacinth, is used extensive particularly in Italian and Greek cooking. The bulbs are boiled then pickled or preserved in oil. They are thought to stimulate the appetite and are also diuretic. Interestingly wild ones are preferred over cultivated ones.

Wild Mustard Blossoms
Mustards are a huge family. They all have yellow to white blossoms, sometimes pink, usually a simple cross which is there the family names Cruciferae comes from. They range from the mustard that produces the seed that makes the condiment to the radish in our salad to the plant that produces what eventually is cleaned and deodorized into Canola oil. In northern climates they are a spring and summer plant, here in Florida they are wintertime fare, showing up after Thanksgiving and usually totally gone by St. Patrick’s day. Wild radish and wild mustard look similar but have small differences. One is that mustards grow tall, radishes like to serpentine. Radish blossoms cluster and have noticable veins, mustard blossoms are singular and the veins are not obvious. The seeds pods are different as well. Mustard’s pod is smooth, the radish jointed and why the mustard is called the charlock and the radish the jointed charlock. Their blossoms are both peppery and mustardy. They work best in cold salads or hot soups, the latter they can be tossed in just before serving. And of course mustard and radish leaves can be cooked up as greens.

White Neem Blossoms
Neem is known for a wide variety of medical uses. There’s hardly any part of the tree that is not employed in some medical use or another. It is also consider a trash tree and a pest in many areas including the Middle East and sub-Saharan Africa. And what few folks know is that the bitter flowers are edible. They are usually eaten with other food as a premeal appetite or a palate stimulant. Botanically the tree is Azadirachta indica, suggesting it’s native to India. In fact, just last week I was given a Neem sapling. It is now happily in the ground. Incidentally, the young leaves are cooked and eaten, the most common way in water buffalo meat salad. Neem honey is prized and the sap is fermented into a local alcoholic drink. If you don’t have your own Neem Tree the leaves and flowers can be bought in Indian markets.

I have read there are no toxic Opuntias. With some 300 of them I don’t personally know. I do eat cactus pads on a regular basis. I fry and grill them. But, as with most cactus, one has to contend with glochids and spines. The spines one can see. It’s the tiny hair-like glochids that can make one semi-miserable, tolerable in a finger, maddening in your tongue. Duct tape removes them moderately well. Wear gloves harvesting. The best approach is to use a long sharp fillet knife as the flowers are surprisingly thick. Also tap them first to dislodge bees. Among all the Opuntia the Prickly Pear Cactus flower is the most often eaten, not raw but cooked, usually boiled. Their flavor leans towards tart. The blossoms also make a good wine.

Oregon Hollygrape
The Oregon Hollygrape is neither a grape or a holly. So much for common names being helpful. It’s the North American equivalent to the Barberry. Beyond cultivation its distribution is a bit strange. One the west coast it runs form California to British Columbia including Idaho, Wyoming, and Albert. On the east side of the continent it goes from Kentucky due north including Canada but not the east coast. Then for some reason it is also in Georgia and New Jersey. The leaves do look like a holly and its name, for a change, suggests that, Mahonia aquifolium. It usually has clusters of yellow flowers around April, depending exactly where you are in North America. The acidic berries are used to make pies,jam, jelly, confections and beverages including wine. The flowers are eaten as is or used to make a lemonade-like drink. Four relative are used in similar ways but none of the others have flowers that are reported as edible. One however, the Mahonia nervosa, has young leaves that can be simmered in water then eaten.

Boil Papaya Blossom, Too
This won’t make much sense to those who live where there is a winter but the first time I climbed Turtle Mound — not a great feat as it is only 80 feet high — I was surprised to see Papaya’s growing on top. Turtle Mound is a midden, an ancient trash heap made mostly of millions of oyster shells dumped there by ancient natives. It’s been more than three decades since my first visit and the papayas are still there, self-seeding as papayas do. A native of Mexico they are naturalized in warm areas of the world. Papaya blossoms, like very young leaves, are edible cooked, which is usually by boiling. Actually cooking the yellow flowers is a lot easier than pollinating them because there are female blossoms, male blossom, and male/female blossoms, kinda you, me and us. You have to move pollenating material around correctly or you don’t get fruit (also edible.)

Perennial Phlox
There are two Phlox, so to speak. One that gets one to two feet high and shows up seasonally in fields, particularly here in Florida. That’s not the one you want. You want the perennial phlox that grows to three of four feet tall, Phlox paniculata. I’m sure you’ve seen it. Like the Meadowsweet above it is an old world plant found in many home gardens and yards. It has escaped into the wild and can be found in the eastern half of North America plus Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska, Utah and Washington state. The slightly spicy blossoms range from red to pink to white. They go well with fruit salads.

Pignut Blossoms
Do you know where the islands of St. Pierre and Miquelon are? Do you know what they are? Among other things they’re the only place in North America where Bunium bulbocastanum is naturalized. The islands are situated at the entrance of Fortune Bay off the southern coast of Newfoundland, Canada. The odd part is they are not part of Canada but still part of France, a tiny toehold still in the New World. Residents are French citizens and vote in French election though the home county is more than 4,000 miles away. It was from these islands that a large amount of Canadian whisky was smuggled in the the United States during prohibition. Easy to grow B. bulbocastanum is called Pignut and Earth Chestnut. It has lacy white flowers similar to Queen Ann’s Lace and attractive foliage. Pignut sets large clusters of small tubers that taste like sweet chestnuts. They are eaten raw or boiled as a vegetable. Leaves can be used like parsley. The seeds and flowers are used for flavoring. British forager Ray Mears included the Pignut in one of his early television series but not in his subsequent books because they taste so good are becoming scarce in England.

Pineapple Weed
Most people don’t think of an edible wild flower growing in the middle of your driveway. Ours was hard-packed sand and gravel and every summer it sprouted and determined crop of Pineapple Weed, Matricaria matricarioides. I noticed our horses, which doubled as our lawn mower, didn’t eat them. That led to my investigation. They are pineapply or applish and related to Chamomile. You might want to avoid them if you have a ragweed allergy.

Pink Wood Sorrel
Wood sorrel, an oxalis, was probably the first wild food that I ate while my parents weren’t looking. A childhood chum of mine, Peter Jewet, and I used to spend summers wandering around the woods and it was he who showed me wood sorrel, though he called it “sour grass.” We didn’t notice that it didn’t look like grass at all. Locally there is one native wood sorrel with a small yellow blossom — edible — and several sorrels from the Caribbean Islands and beyond. They all have large pink blossoms, hence Pink Wood Sorrel, and make nice, tart additions to salads. They are like rhubarb lite. See my full article on side and video.

Chickasaw Plum Blossoms
Read this next entry carefully: You can eat some Plum blossoms, a few, a half dozen, but not a lot. Why? Because they have a chemical which when it goes through your tummy tum tum produces cyanide. A little cyanide we can tolerated, a lot will make you ill. Too much and you are deceased though admittedly it would take a lot of plum flowers to do that. Plum flowers are a trail side nibble, a sprinkle in salads or on a dessert. Sparingly is the key. They are sweet, taste like nectar. Which plums? As far as I know any plum that produces plums, that is, in the genus Prunus. It should hold true for cherry blossoms as well as they are in the genus Prunus as well but I really don’t know.

Puget Balsam Root
The Puget Balsam Root aka Deltoid Balsam Root is strickly a west coast of North America plant. In the sunflower family Balsamorhiza deltoidea was a food and medicinal plant for Native Americans. Young tender roots are eaten cooked, like carrots, or candied. The natives also roasted and ground the root using it like coffee. The young leaves were boiled as a potherb and the plant’s oily seeds eaten like sunflower seeds. The flowerstalk can be cooked and eaten like a vegetable.
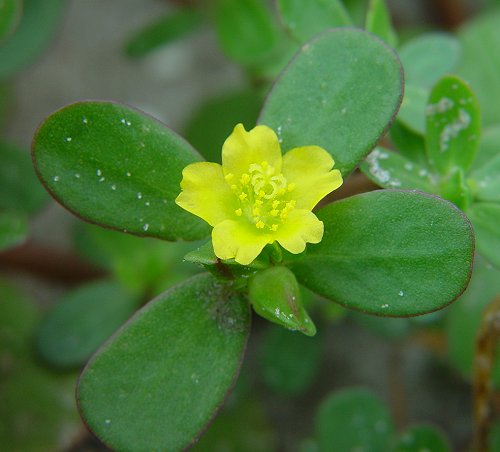

Purslane’s Small Blossom
It was something of a debate, to make this entry or not. After all, Purlane is one of the most esteemed wild and cultivated edibles in the world (except oddly the United States.) It is used as a salad ingredient, a vegetable, a soup thickener, a flour, and a pickle. And yes, the flowers are edible but they are only open for a day. And when I say purslane I mean Portulaca oleracea, the kind with yellow blossoms only. Yes, I know there are commercial cultivars of multiple colored blossoms and they might look wonderful in a salad. But, I don’t know if they are edible. The Moss Rose/Rose Moss, another wild Purslane, Portulaca pilosa, is in my estimate not edible. So I stick with the original, common purslane with the yellow blossom. They are edible raw and cooked. Incidentally, the tiny pink blossoms of the sea purslane, Sesuvium portulacastrum, is also edible raw or cooked.

Queen Ann’s Lace
Among the wild flowers I played with as a kid was Queen Ann’s Lace, the wild carrot. It’s bird’s nest blossom with a red dot in the middle was easy to identify. It’s also hairy and smells of carrots. Perhaps surprisingly, it’s not native to North America but an import from Europe. Centuries ago the modern carrot was cultivated from the Queen Ann’s Lace, and by the way, the green tops of the cultivated carrot are edible as a flavoring or a green, if they are raised in a wholesome environment. The blossoms of Queen Ann’s Lace is carrot flavored and strong. Use sparingly until you are used to it. Also make sure you are not picking poison hemlock blossoms. The wild carrot smells of carrot, the stem is hairy, and look for a red dot in the middle of the blossom. Poison hemlock has none of these.

Rocky Mountain Columbine
Sometimes within a genus there will be toxic species and edible species. The Aquilegia are that way. Most of them are toxic with alkaloids, four are not, one in east Asia, three in western North America. Thus making sure you have the exact species is quite important. Close is not good enough. Edible in North America is Aquilegia caerulea, the Rocky Mountain Columbine. The nectar-heavy flowers are eaten as a snack or tossed into salads. They also make a good jelly. The Hanaksiala Indians got nectar from the blossoms of the A. formosa (Western Columbine) while the Miwoks boiled and ate the early spring greens of the A. formosa var. formosa (Crimson Columbine.) In eastern Asia the species is A. buergeriana, also called Yama-odamaki. It’s sweet flowers are sucked for their nectar and also used in salads. The leaves are also edible. One other columbine might have edible uses. A. canadensis root was reportedly eaten by Native Americans.

Salsify, Tragopogon porrifolius
It’s other names include Goatsbeard, Oyster Plant, Vegetable Oyster, Jerusalem star, Purple Oyster Plant, and Meadow salsify. Commoningly called just Salsify, botanically it is Tragopogon porrifolius. As you might have surmised to some the root tastes faintly of oysters, to others parsnip, and probably to some like oystery parsnips. Native to the Mediterranean area it has been introduced to Great Britian, northern Europe, South Africa, Australia, Canada and the United States. It is found in almost all the states including Hawaii but excluding the Old South except Georgia which has it. Roots are eaten raw in salads, or they are boiled, baked, and sauteed. They are added to soups or can be grated and made into cakes. Flower buds and flowers are eaten raw in salads or cooked then cooled and added to salads. The flowers are also pickled. Young flower stalks are cooked and dressed like asparagus. Sprouted seeds are put in sandwiches or in salads. The sap can be used as gum. Bradford Angier, a well-known Canada-based forager, says the yellow salsify is also edible.

Samphire Blossoms
I have a soft spot for edible plants that grow that can grow in salty places. They are usually fleshy, salty greens edible raw or cooked. A traditional seaside green is Samphire, Crithmum maritimum. At one time it was sold under the name of Crest Marine. It has fleshy, aromatic leaves that are spicy, peppery. The stems, leaves and pods can be pickled and the leaves are used fresh in salads. They can also be boiled as greens. In Italy and Greece the leaves are cut into small pieces, mixed with olive oil and lemon juice making a salad dressing. The raw blossom are used in salads. Very high in Vitamin C. The name, Samphire, is a French corruption of St. Pieere, (St. Peter) patron saint of fishermen.

Sego Lily
The second mariposa is called the Sego Lily, Calochortus nuttallii, and is not related to the palms or cycads which are spelled Sago. The bulbs of the Sego Lily are excellent raw, fried or boiled. Preferred ways of cooking include steaming them in pits or roasting them over a smoky fire, each method creating special flavors. The seeds are ground into meal and the whole plant can be used as a pot herb. The flowers and flower buds are eaten raw as a trail nibble or in salads. The Sego has a larger range than its kin above, farther east and west.

Smartweed
This next blossom is either love or hate in my foraging classes, the Smartweed, or Polygonum. I ask for a student volunteer to try a small amount. I usually also ask for someone who likes hot peppers then have them chew a very small portion of a leaf. It has a slow-to-get-started burn but then it grows like a red pepper heat rather than black pepper. The blossom are even hotter and fire up quicker. But, they have a bitter after taste and a perfume quality. Several of the Polygonum species heat up. The heat varies species to species. In some the leaves ca also be used as a green but they are a vasoconstrictor, read they can raise blood pressure in some.

Sesbania grandifolia
Sesbania grandifolia has managed to work its way into warmer areas of the world. If you have a frost you might be able to pot it but you won’t find it out in the field. Originating in either India or southeast Asia, it grows best in hot, humid areas.The shrubs long narrow pods are eaten as a vegeetable dish, similar in use as string beans. The seeds are fermented into a tempeh turi. Young leaves and shoots are eaten in salads or as a pot herb or in soups and stews. Sesbania grandifolia flowers are eaten raw in salads, boiled, fried or use in curries, stews and soups. They taste like mushrooms and are rich in iron and sugar, read sweet.

Spanish Needles, Beggar’s Ticks
Bidens alba, also known as Spanish Needles and Begger’s Ticks, has a piny flavor, resinous. There are several daisy-like Bidens around the world, white or yellow, few petals or many. Flowering year round in warmer climates, the blossom’s plant was recommended some 50 years ago to become a commercial crop. Because it grows in so many places for free that never happened. While Spanish Needles blossoms are salad fare, they hold their flavor while cooking and can be added to a variety of dishes.

Spiderwort
Every time I see a Spiderwort I think of Pocahontas, the Indian maiden who save the life of Captain John Smith (see my separate article about them and spiderworts.) There are many reason to praise the mild spiderwort. Its blossom can be candied or tossed plain into salads to add color. There are also ruby and white spiderworts. The blossom are open for only a day but that’s okay because the spiderwort has many blossoms waiting to open. With no particular flavor though with a hint of sweetness the flowers are available throughout their growing season. Pictured are blue, white and red spiderworts but usually they are blue.

Star of Bethleham
The Star of Bethleham started out in central and southern Europe, North Africa, southeast Asia and presumably Levant. When it came to North America is not known but it escaped. Now it is found in most of North American except the Rocky Mountain states and due north into Canada. Botanically Ornithogalum umbellatum the cooked bulbs are sometime eaten. Raw bulbs have been implicated in animal poisonings.We, however, are more interested in higher up. The flowers are traditionally eaten baked in bread. The unopened inflorescence of a relative, Ornithogalum pyrenaicum, are cooked and served like asparagus. It’s a seasonal food in southwest England around Bath and Bristol.

Wild Strawberry Blossom
There’s a real good reason why almost no one knows this next wild flower is edible. And that’s because nearly everyone eats the fruit! Strawberries are prime food. BotanicallyFragaria virginiana, the blossomes are edible raw though most folks wait for the fruit. Of course, you can be different and toss the flowers on salads just to surprise folks. The leaves are edible as well but are on the astringent side. As with many cultivated crops harvest carefully because as a commercial crop they are often doused wth this or that chemical to keep them living and looking well until they get to market. The cultivated blossoms are pink, the wild white.

Spring Beauty
The Spring Beauty, also Springbeauty, Clayt0nia virginica, is a longtime standard for foragers. They are abundant in some areas, rare in others. Thus forage with some local consideration. True to its name the attractive wild flower is a sign of spring and easy to recognize from other spring blossoms. The white to pink petals have pink stripes, sometimes pale, sometimes bright, but pink stripes nonetheless. Each blossom also only has two sepals (leaves right under the blossom.) Lower leaves are strap-like varying in size and width. The plant grows small roots that remind people of tiny potatoes, hence the nickname “Fairy Spuds.” The flowers as well as the parts above ground are edible raw or cooked. There are several edible Spring Beauties, see separate article on site.

Sweet Goldenrod
As you might assume the Boston Tea Party of 1773 reduce the colonists store of tea, and think how far that tea had come, from the other side of the world by sailing ship. It wasn’t as if a new shipload was arriving anytime soon as a replacement. The colonists, already an irritated independent lot, came up with their own “Liberty Tea” and even shipped it to China. Called into action was the Sweet Goldenrod, and not just any Goldenrod but the Solidago odora. While it is reported you can make a tea out of any Goldenrod the top of the botanical heal is the S. odora because it tastes like anise. The flowers and the leaves can be used to make tea.

Sweet Woodruff
Several Galiums grow here in Florida, one of which can be used for dye, Galium tinctorium, and one of which is edible, Galium aparine. Easy to sort out the two. If you can find whorls of five leaves it is the G. tinctorum. If you can find wohorls of seven leaves, its the G. aparine, among other characteristic. Their blossoms are really to tiny to attend to. The favored Galium, however, does not grow here but I have run into it elsewhere, Galium odoratum. Imported from Eurasia and now naturalized it grows roughly in the northeast quadrant of North America and is commonly called Sweet Woodruff, or Wild Baby’s Breath. It’s been used a lot in Europe as a flavoring particulary in German May wine. Its flavor is sweet and vanilla-like which brings us to a warning. One of the chemicals that gives it a sweet smell is coumarin. Taken in large quantities it reduce the blood’s ablity to clot. Flavoring and a few blossom here or there is not a worry unless you are in frail health and already taking blood thiners.

Tiger Lily
Many lilies are called the Tiger Lily but botanists argue there is only one, Lilium landifolium, a native of Asia and Japan but naturalized in the northeast quarter of North America, among other places. Almost all of the Tiger Lily is edible, bulb to flower. In fact it is a cultivated crop in Asia and Japan turnips or parsnips in flavor. Flower buds are eaten raw or cooked, as are the flowers. The pollen is edible as well. Yes, I know there are dire warnings on the Internet that it is poisonous for humans but evidence of that is absent. It IS toxic to cats. One way to identify this lily from the natives is small black bulbils on the stem. While it is naturalized it usually does not go far from urban areas. When I used to traipse around the countryside in New England I always found these and daylilies near old or abandoned farms. In fact, out in the country they were usually right across the road from the farm house. See full article on site.

Tipo Tambo
For a plant that has been cultivated for thousands of years Tipo Tambo, Guinea Arrowroot, Calathea allouia, is little known and raised only by subsistence farmers. What they know that few others don’t is that the plant’s crisp tubers taste like sweet corn and rival any gourmet hor d’oeuvres in flavor and texture. The leaves are used like tamales wrapping food to impart flavor. And of interest to us young flower clusters are cooked and eaten. The roots are a traditional Christmas food in the Dominican Republic. The species has been distributed around the world and is found in warm climates. The roots keep their crisp texture even after long cooking. They are usually boiled 15 to 20 minutes. As well as being eaten on its own, they are often an ingredient of salads, mayonnaise and fish dishes.

Tulip Tree Blossom Nectar
The blossom of the Tulip Tree, Liriodendron tulipifera, is not edible as far as I know nor would I try it. Other parts of the tree have a heart-stimulating alkaloid that is best avoided. But the flower nectar is drinkable. For just a short time while the tree is blossoming there is a small amount of very sweet nectar in each blossom. It is heavy and honey-flavored. You can drink it directly from the blossom. While early reports say the native made honey from the blossom what they were really doing was collecting nectar. The tree was also called the Sap Poplar, perhaps because its sap is consumable. I don’t know and have not found any reference to said but it wouldn’t surprise me. As a source of nectar the tree also attracts hummingbirds, squirrels and is a host plant for tiger and spicebush swallowtail butterflies.

Wapato, or Wapati
Among the wild flowers I have tasted the white petals of the Wapato are a first rate delicacy. The plant itself is known for its egg-sized tubers that arrange themselves around the base like numbers on a clock. Its blossoms are very distinctive. The only problem getting to Wapato, or Wapati, is as they like to grow in water but you can often find them close to the bank. Take only the petals of the blossom. They are sweet and fragile, tasting a bit like marshmallow. No cooking here. If you use them in a salad put them on top or they will get lost.

Water Hyacinth
The most “noxious” weed in the world has edible flowers, and leaves and bottoms. It is also illegal to possess. Follow my motto: “No witnesses, eat the evidence.” I doubt anyone would be prosecuted for eating a weed nearly every regulatory agency wants to get ride of, the Water Hyacinth. Depending upon your perspective it is either a usable biomass that can replace itself in three weeks or its a horrible weed to be done away with. The state of Florida estimates that if it did not spend millions annually and stopped fighting it the aquatic denizen would within three years clog all freshwater bodies and rivers in the state to the point of not usable. Do your civic part by picking the blossoms and cooking them like a vegetable. Their flavor is mild. Note one easy identifying characteristic is that the blossom’s top petal has a yellow spot.

White Sagebrush
The White Sagebrush is found throughout most of North America except Florida, Georgia, West Virgina, Alaska, the Yukon Territory, and extreme eastern Canada. Called Artemisia ludoviciana, it has also become a favored garden plant though most people have no idea of its uses. Thirteen species in the Artemisia genus were used by the Native American groups for a variety of medicinal, veterinary, and ceremonial purposes. The Apache, Chirichua and Mescalero used the plant to flavor meat. The Blackfoot chewed the leaves like candy. The flowerheads can be used as seasoning or to make a tea. It has many cultivars

Wild Rose, not Irish
Wild Roses were a common flower behind the house I grew up in though I often wondered why they flat and pink compared to the ones sold in flower shops. I learned why decades later when I got accepted to law school. The job I had stopped before classes began so to tide me over I delivered flowers. One could tell several stories regarding that including how most women are very suspicious when they get roses from him other than Valentine’s Day. I even had some deliveries refused! Beyond that, however, the tall red roses I delivered, so different than the ones of my youth, had no scent. None. Zip. Zilch. Nada. No rose aroma at all. Just before I would deliver them I’d take them out of the van and spray them with an artificial rose aroma. The roses were raised for their look and in the process the scent was bred out (and you did not spay them in the van or you smelled roses for weeks.) Less purebred roses are known for their rose hips and edible petals. The flavor depends on the type, color and conditions of raising. They can range from tart to sweet, spicy. Darker ones have stronger flavor. Remove any white portion of a petal. That will be bitter. All true roses (genus Rosa) are edible.

Wild Violets
Wild Violets are a difficult topic to tackle because there are so many, and, because they are also a common flower and a commercial product. For example, higher up in this article are Johnn-Jump-Ups, which are violets and in Edible Flowers Part Six I mentioned pansies which are descendants of Johnny-Jump-Ups. It’s a botanical case of yours, mine and ours. There are some 500 species of violets, probably all of them edible (note African Violets are NOT violets nor edible. Also the roots of Violets [Viola] are not edible. The American Indians used them for insecticides.) Edible violets are in the genus Viola. But there are some things one can say about them. First the Roman’s loved violet wine and made so much of it they nearly had civil wars over it. And by tradition violets are the flower of choice for composer Chopin’s grave in Paris. Short violets tend to be sweeter, more flavorful and aromatic than taller species, with exceptions. And yellow violets in more than moderate quantities can be laxative. Long-time forager Dick Deuerling tells a story about violets and boy scouts. He was leading the scouts on an all day hike when in mid-afternoon they came upon a huge patch of violets. The boys ate their fill and because of the sugar content went right to sleep! Dick said he had a hard time getting them up to finish the hike.

White Trout Lily
Our next two blossoms are in the same genus, Erythronium. The White Trout Lily is E. albidum and the Yellow Adder’s Tongue is E. americanum. First the White Trout Lily: Flower stalks, flowers, buds and the white bell-shaped flowers can be eaten raw or cooked. The young leaves are edible raw as well. They are crisp, tender, and tasty. However, the plant only has two leaves so if you are going to harvest them harvest only one per plant. The bulbs are also edible after boiling. They are considered delicious. However, in larger amount they can be emetic so consume within reason.

Yellow Adder’s Tongue
The Yellow Adder’s Tongue is slightly different. Like its relative its flower stalk, flower buds, and flowers are edible raw or cooked. The leaves can be eaten raw, such as in salads. Again, the plant only has two leaves so harvest responsibly. E. americanum bulbs can be eaten raw or cooked. They are crisp and chewy. However again, consume sparingly as they can be emetic. A third Erythronium, a European, E. dens-canis, the Dog’s Tooth Violet, also has edible cooked roots. It is also the source of starch use to make pasta like noodles or cakes. Leaves are eaten boiled. Don’t let the common name of the E. dens-canis — Dog’s Tooth Violet — confuse you regarding violets, that is in the genus Violas. Violas do not have edible roots.

This plant is used so much it’s surprising the flower has managed to put itself nearly everywhere, field and farm. Yarrow (Achillea millefolium) is found throughout North American and many parts of the world. Young leaves are eaten in salads, or cooked as a vegetable, or added to soups and stews. The leaves and flowers are brewed into a tea. Sometimes in beer making it is substituted for hops. An oil from the flowers is used in flavoring a variety of commercial drinks and alcoholic beverages. It’s primary use for our purposes is blossoms to make tea.

Yellow Dayflower
I know I mentioned Dayflowers earlier but I thought a recent discovery deserved its own entry, the Yellow Commelina, or Commelina africana. I was teaching a class in tamp when a student said “what is this?” A low-growing salmon to yellow blossom was looking up at me. I recognized what I thought to be the genus immediately, Commelina but I have never seen or heard of a yellow one. A bit of research identified it. The question is how did it get to Florida? It is listed as one of Africa’s resources and edible cooked including the root. Can be confused with Aneilema aequinoctinale.

Yellow pond lilly
While the Yellow Pond Lily has been on the move. It’s been Nuphar Luteum, Nuphar lutea, Nuphar lutea var. advena and Nuphar advena. The latter will probably stick for a while. Genetically it never was Nuphar luteum/lutea. Indeed, the Yellow Pond Lilies in North America might go from one wrong species to eight new right ones, once the botanists have argued it all out. One hint that the yellow pond lilies in North America were different than the yellow pond lilies of Europe ws the total lack of their use in Europe and their common use “across the pond.” While the local root is too bitter to eat it’s seeds are only mildly bitter and can be soaked to get rid of that quality. See my article on the Yellow Pond Lily. The large-petaled yellow blossom of the Nuphar advena can be used to make a tea.

Yucca
I have read in many a foraging book that Yucca blossoms are edible raw, and many are. The ones that grow in my area, Yucca filamentosa, are not, which is unfortunate. They have a wonderful crunchy texture, and a sweet taste. You really want to eat them. But the Y. filamentosa also has saponins, call it plant soap. After eating one you soon get a bitter astringency in the back of your mouth and throat, like you got when as a kid you utter a dirty word and mom had you taste a bar of soap. It brings back those days. So yes, yucca blossoms are edible raw, but try yours first, just a little. Then wait half a minute to a minute. If all is well, enjoy. My local blossom while not pleasant raw does cook up nicely. I boil them for a few minutes and then use them in several dishes.
 All of Green Deane’s videos are available for free on You Tube. They do have ads on them so every time you watch a Green Deane video I get a quarter of one cent. Four views, one cent. Not exactly a large money-maker but it helps pays for the newsletter. If you want to see the videos without ads and some in lightly better quality you can order the DVD set. It is nine DVDs with 15 videos on each. Many people want their own copy of the videos or they have a slow service and its easier to order then to watch them on-line. They make a good gift for that forager you know. Individual videos can also be ordered. You can order them by clicking on the button on the top right of this page or you can go here.
All of Green Deane’s videos are available for free on You Tube. They do have ads on them so every time you watch a Green Deane video I get a quarter of one cent. Four views, one cent. Not exactly a large money-maker but it helps pays for the newsletter. If you want to see the videos without ads and some in lightly better quality you can order the DVD set. It is nine DVDs with 15 videos on each. Many people want their own copy of the videos or they have a slow service and its easier to order then to watch them on-line. They make a good gift for that forager you know. Individual videos can also be ordered. You can order them by clicking on the button on the top right of this page or you can go here.  “Did you ever eat a larch?” was the subject of this recent post on the Green Deane Forum (the button to join the forum is on the right hand side of this page.) Euell Gibbons got a lot of mileage from asking “did you ever eat a pine tree?” But what of the larch? There was a stand of them — a Larchhurst — about 300 feet from the front door where I grew up. One of the first things I noticed was it was a conifer that was not evergreen. It loses its “needles” in the winter. And local folks didn’t call it Larch. It was a “hatmatack” or “tamarack.” These trees can live 700 years, or so the experts say. The sap is edible and the inner bark in spring. Young shoots were cooked as vegetables. Lumps of sap were also chewed like gum. The dried sap was used like baking powder. These things I did not know when I was young though I did know it did not size up well for the wood stove. We heated and cooked with wood and my job (besides feed five horses every day and haying) was chopping wood, cord after cord of wood. I AM dangerous with an ax. What caught my interest in the larch recently is arabinogalactan. I won’t even try to figure out how that is said. Perhaps a chemist can help.
“Did you ever eat a larch?” was the subject of this recent post on the Green Deane Forum (the button to join the forum is on the right hand side of this page.) Euell Gibbons got a lot of mileage from asking “did you ever eat a pine tree?” But what of the larch? There was a stand of them — a Larchhurst — about 300 feet from the front door where I grew up. One of the first things I noticed was it was a conifer that was not evergreen. It loses its “needles” in the winter. And local folks didn’t call it Larch. It was a “hatmatack” or “tamarack.” These trees can live 700 years, or so the experts say. The sap is edible and the inner bark in spring. Young shoots were cooked as vegetables. Lumps of sap were also chewed like gum. The dried sap was used like baking powder. These things I did not know when I was young though I did know it did not size up well for the wood stove. We heated and cooked with wood and my job (besides feed five horses every day and haying) was chopping wood, cord after cord of wood. I AM dangerous with an ax. What caught my interest in the larch recently is arabinogalactan. I won’t even try to figure out how that is said. Perhaps a chemist can help.